IUI Treatment
Purpose
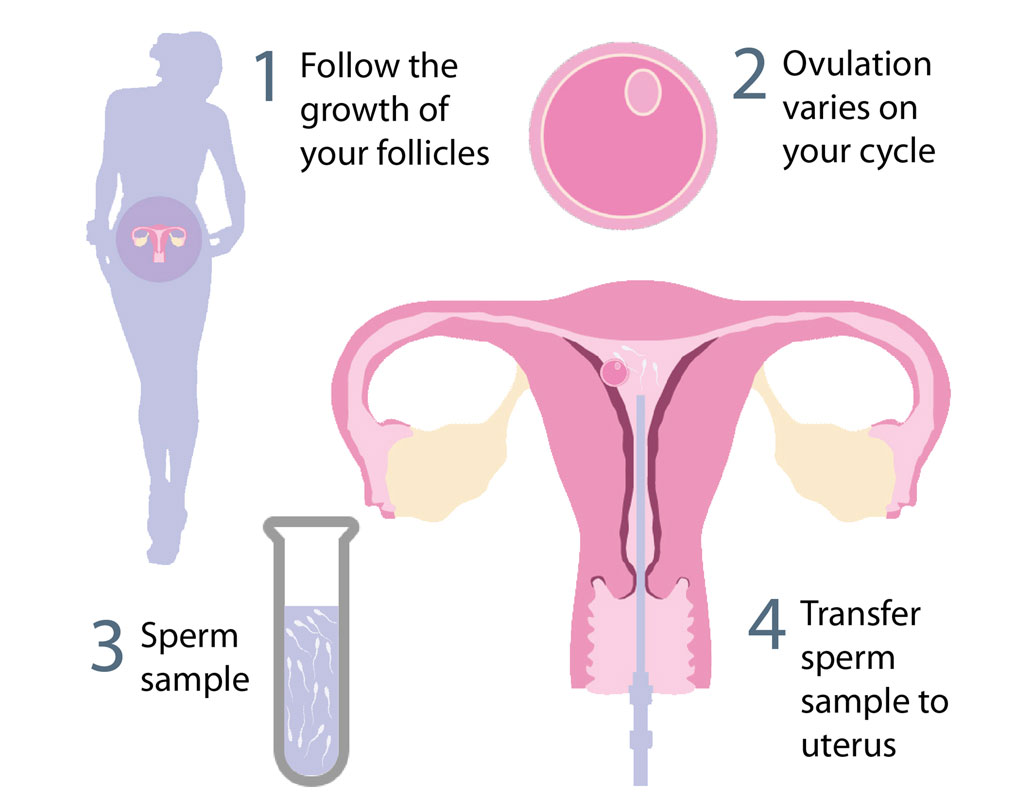
Intrauterine Insemination commonly known as IUI is one of the many assisted methods of conception where concentrated and washed sperm is placed directly inside the uterus around the time when the ovary releases eggs to be fertilized. This is done in case of failed natural attempts or low sperm motility.
Why IUI
An Intrauterine Insemination is useful in such cases where the pregnancy has a good chance of going smoothly, but fertilization is proving to be a challenge.
For this, the sperm count, the motility and sperm quality has to be tested in men, and for women the general health of ovulation, patency of tubes, cervical factors, and presence of anti-sperm antibodies. need to be checked.
What you can expect
It should be kept in mind, that the window of time for fertilization is just a little more than 12 hours from the release of the ovum. To maximize the chance of fertilization, the menstrual cycle is closely observed with the help of ovulation kits, blood tests, ultrasound scans and also basal body temperature. The colour and texture of the vaginal mucus are noted, as is the of the nose of a woman’s cervix.
Generally, to improve the chances of artificial insemination, drugs that help create a stimulated cycle may be used.
Results
Intrauterine Insemination is said to be a more effective method of artificial insemination, than Intra Cervical Insemination. This is because the introduction of sperm directly into the uterus increases the chance of fertilization considerably.
Your treatment cycle (and how
many cycles you plan to do) will depend on why your doctor has recommended IUI and on other medical conditions of the couples.
IUI+Donor sperm
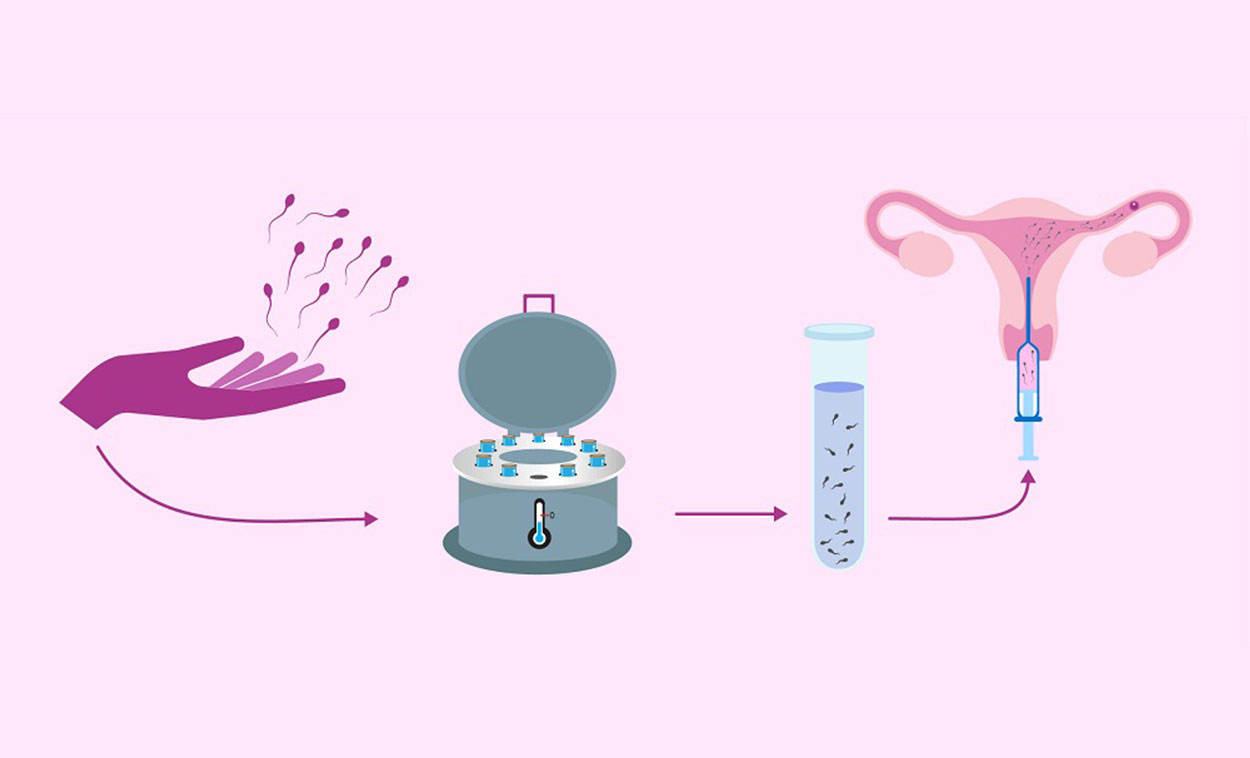
Donor insemination is the use of artificial insemination – typically intrauterine insemination (IUI) – using donor sperm. Natural conception is dependent on having a certain number of moving sperm. If the numbers are too low to even consider insemination using your partner’s sperm, then we will typically recommend in vitro fertilization (IVF), possibly with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). If, however, your partner has essentially no sperm or if IVF is not a financially viable option, donor insemination may be offered as an alternative.
Sperm donors are typically less than 40 years of age to minimize the potential risk of genetic abnormalities associated with aging. Usually donors are anonymous (unknown), though occasionally a known donor might be used. A sperm donor has to undergo rigorous blood testing to minimize the risk of transmitting a communicable disease.




