- Ovulation Induction
- Egg Freezing
- TESA / PESA
- Micro TESE
- ERA
- PGD
- Embryo Donation
- Hysteroscopy
- PAP Smear
- Gynaecology
- Surrogacy
- Endometrial Scratch
- Genetic Evaluation
- Male Infertility
- Recurrent pregnancy loss
- Sexual Dysfunction
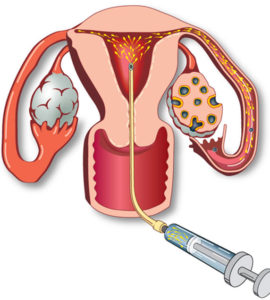 Ovulation induction- timed intercourse (OI-TI)
Ovulation induction- timed intercourse (OI-TI)
Is one of the simplest forms of assisted reproduction techniques. It’s a relatively inexpensive procedure, with very little inconvenience and minimal risk of complications.
The procedure is ideal for young patients with healthy reserve, PCOS or unexplained infertility without other coexisting medical conditions.
Why it’s Done
All that is needed in some couples to conceive is to identify the correct time to have intercourse to maximize the chances of conception. In OI-TI a fertility specialist tracks the processes of ovulation and advises a couple on the right window to conceive naturally.
The couple would be advised intercourse during a window immediately prior to ovulation and for 2 days post ovulation. As the sperm survives in the female reproductive tract for up to 72 hours, the chances of the released egg being fertilized by the sperm naturally is enhanced.
What you can expect
The treatment of OI-TI would usually start on the second day of the menstrual cycle. Your reproductive medicine specialist would advice you to see her in the clinic on day 2 or day 3 of your menses for a ultrasound scan and to plan your medicines. Your reproductive medicine specialist would then advice you on the course of medicines to take and the frequency of scans to track your progress.
The medicines used in ovulation induction allow a specialist to control the process of ovulation. The processes of ovulation is tracked by a fertility specialist using a ultrasound scan. The medicines (either tablets or injections) would have to be taken daily for about 8-14 days.
The specialist with track the process of ovulation and advise the couple on the correct days for intercourse so as to maximize the chance of conception.
Results
Your reproductive medicine specialist would advice you to check for pregnancy after 14 days with a pregnancy kit or blood test. Delay in your next periods is a possible indication of pregnancy. Many reproductive medicine specialists try OI-TI cycles 2-3 times in appropriate patients before trying more advanced assisted reproduction techniques.
What Are the Risks?
You do not become pregnant (failure): No assisted fertility technique guarantees success on the first attempt. Do not be discouraged by a negative result. The aim of the procedure is to provide a chance for natural conception.
There is a rare chance (1 in 1000 patients) where you react more strongly to medications than what is expected. This would cause multiple follicles in the ovaries to come up rather than one or two. Your doctor would advise you medical treatment and possibly an alternate procedure such as IUI or IVF in such cases.
 Egg Freezing
Egg Freezing
Egg Freezing is a state-of-the-art technology that allows women to store their fertility in a time capsule, without the gnawing worry of their eggs diminishing in quality as they age. By freezing your eggs in advance, you can choose to ride the parenting wave whenever you’re ready. This way, you don’t have to play a perpetual game of ping-pong with your biological clock.
Is Egg Freezing A Right Process?
The stress of keeping up with your biological clock can be overwhelming. And yet, you may find that there’s so much life to live before you can even think of having a baby. By considering vitrification, you can make time for the things that feature higher on your priority list. When you finally do reach a stage where you’re ready to start a family, you can trust us and Your eggs will be waiting.
Limited Supply of Eggs
The number of eggs that your ovaries house is finite. Naturally, as you age, this reserve of eggs steadily depletes. In turn, the chances of conceiving a baby decline with age. Freezing your eggs can ensure that healthy eggs are extracted and stored for later use.
Diminishing Quality Of Eggs
As ovarian reserves decline, there is a corresponding fall in their quality. Lower quality eggs can lead to chromosomal abnormalities and an increased risk of miscarriage. By opting for vitrification you can guard your current set of healthy eggs and save them or later.
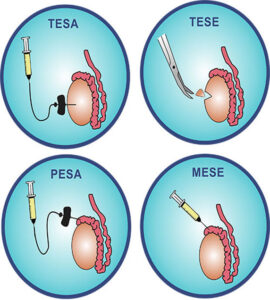 TESA-PESA-MESA Treatment: Sperm Extraction Procedures
TESA-PESA-MESA Treatment: Sperm Extraction Procedures
What are these TESA and PESA procedures?
Some of the causes of male infertility are non availability of normal viable sperms in the ejaculate for IVF treatment.
Some of the reasons could be:
- Azoospermia (No sperms),
- Low sperm count (Oligospermia),
- Low sperm motility (asthenospermia).
Tesa and Pesa treatment includes the procedures to recover sperms through the minor medical surgical process.
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration)
PESA treatment is a surgical procedure which involves the use of needle and syringe technique as for a needle biopsy, but the needle is directly placed into the epididymis. This often gives good results if there is a blockage in the vas deferens but the testis is producing sperms.
TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration) and TESE
(Testicular Sperm Extraction)
TESA Treatment is similar to a needle biopsy but involves placing a needle attached to a syringe through the skin of the scrotum, and simply sucking out the fluid from the testicle.
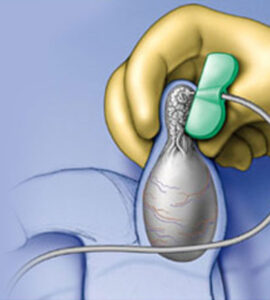 MICRO TESE
MICRO TESE
Sperm can be retrieved directly from the testis rather than from the ejaculate. These procedures are often called TESA (testicular sperm aspiration), TESE (testicular sperm extraction) or PESA (percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration) or Micro-TESE.
The most common reason is because sperm are not present in the ejaculate. This can be because the vas deferens (the tube which carries sperm from the testis) can be blocked due to a vasectomy or if the man is a carrier of the genes for cystic fibrosis. Sometimes the sperm are present in the testis in very low quantities and are not seen in the ejaculate.
micro-TESE is performed under general anaesthetic by a surgeon (usually a urologist) using an operating microscope. A scientist takes samples and seeks live sperm in the samples removed from the testis. This is highly skilled work which takes a long time.
Sperm obtained through TESE and micro-TESE can be used directly if there’re fresh or frozen oocytes (eggs) available or sperm can be frozen. Fertilization of the eggs is by injecting the sperm directly in the eggs in a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
 Endometrial receptivity array (ERA)
Endometrial receptivity array (ERA)
Endometrial receptivity array (ERA) is a diagnostic procedure that may help determine whether the endometrial cavity is ready for embryo implantation.
- ERA endometrial biopsy is a relatively new procedure, which involves biopsying a small sample of the endometrium, or lining of the uterus, for molecular analysis.
- Problems with the endometrial lining are one of the causes for infertility in women with recurrent pregnancy loss or multiple failed in vitro fertilization (IVF) transfers.
Physicians use ultrasound technology to examine the thickness and pattern of the endometrial lining in preparation for embryo implantation during an IVF cycle. Although ultrasound is an established entity, there is a subset of patients who have an appropriate endometrial lining and transfer of morphologically high-quality embryos, who fail to successfully conceive and have a live birth following an IVF cycle.
It is thought that some patients may have alterations of their “window of implantation” that may decrease their implantation rate and pregnancy success using traditional ultrasound and hormone assessment.
ERA biopsy may be an option for women already undergoing infertility treatment and is typically recommended for women who have had previous IVF cycle failures or have experienced miscarriage or recurrent pregnancy loss.
 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a procedure used prior to implantation to help identify genetic defects within embryos. This serves to prevent certain genetic diseases or disorders from being passed on to the child. The embryos used in PGD are usually created during the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a procedure used prior to implantation to help identify genetic defects within embryos. This serves to prevent certain genetic diseases or disorders from being passed on to the child. The embryos used in PGD are usually created during the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Why it’s Done
PGD is recommended to couples are at risk of transmitting a known genetic abnormality to their children.Only health and normal embryos are transferred, thereby decreasing the risk of transmitting mutated gene.
Primary candidates for PGD
- Couples with a family history of X-linked disorders (Couples with a family history of X-linked disease have a 25% risk of having an affected embryo [half of male embryos]
- Couples with chromosome translocations, which can cause implantation failure, recurrent pregnancy loss, or mental or physical problems in offspring
- Carriers of autosomal recessive diseases (For carriers of autosomal recessive diseases, the risk an embryo may be affected is 25%.)
- Carriers of autosomal dominant diseases (For carriers of autosomal dominant disease, the risk an embryo may be affected is 50%.)
Conditions diagnosed using PGD
PGD should be offered for 3 major groups of disease:
- sex-linked disorders
- single gene defects and
- chromosomal disorders.
What you can expect
The PGD test cycle is explained to prospective parents as it involves multiple steps.
- CaseReview
Each PGD test is custom- designed on the specific disease and mutation that is inherited in a family. The proband or couples genetic test results will be reviewd and the case accepted if PGD is possible. DNA samples from the couples as well additional family members like parents or affected child will be required. This proces will take 4-5 weeks
- Stimulation of ovaries
- Egg collection
- Fertilization
- Culture and Biopsy
- PGD testing
- Embryo transfer
- Pregnancy
Results
Positive Results: Affected Embryos which carries the mutated genes, embryos are not recommended to transfer
Negative Results: Non affected Embryos which doesnot carries the mutated gene, embryos are recommended to transfer.
Risks of the procedure
Most of the risks invloved in PGD treatment are similar to those for conventional IVF which invloves:
- Risks of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome,multiple pregnancy, and increased risk of birth defects not related the genetic test.
- Risk of biopsy or freezing harming the embryos.
- False negative results, where an abnormal embryo is transferred to the uterus, resulting in possible miscarraige, and health embryos are dicarded, limiting chances of healthy pregnancy.
- Test could reveal there are no normal embryos to transfer.
 EMBRYO DONATION
EMBRYO DONATION
If you’re trying to have a family and it isn’t happening the way you planned, embryo donation might be a good option. There’s a lot to learn about the process and a lot to consider in the decision. RESOLVE wants to ensure that women and men facing infertility are fully informed about all aspects of embryo donation as a family building option.
When a couple or individual undergoes in-vitro fertilization treatment for infertility, they are able to cryopreserve any embryos not transferred during that cycle for use in a subsequent cycle. And while the majority of these frozen embryos are intended for use by the couples who created them in IVF treatment cycles, thousands are potentially available for embryo donation to other infertile patients. Couples struggling to build a family can consider embryo donation as a viable option.
 HYSTEROSCOPY AND LAPAROSCOPY SURGERIES
HYSTEROSCOPY AND LAPAROSCOPY SURGERIES
Infertility is symbiotic with anomalies in the womb or abdomen. Two primary procedures are employed to detect inconsistencies in these areas. A hysteroscopy is performed with the aim of examining potential problems in the uterus that may be leading to infertility. It is done using a fine device known as a hysteroscope, which is clipped with a tiny camera and light on its beak. It is then passed through the vagina, upwards towards the endometrium. Similarly, a laparoscopy procedure is a keyhole to a woman’s abdomen and pelvic region and is especially useful to treat cysts, endometriosis and fibroids, in addition to a host of other conditions. This technique uses a laparoscope, a lightweight tool that is inserted through incisions made in the abdomen, to view an array of organs.
WHY CHOOSE HYSTEROSCOPY AND LAPAROSCOPY SURGERIES?
A hysteroscopy and a laparoscopy usually go hand in hand, working together to provide your fertility consultant with a view of your endometrial landscape. There are several reasons why these procedures may be recommended.
ANOMALIES IN UTERUS
In some cases, the shape or size of the uterus may be out of the ordinary, proving hostile for an embryo. In other cases, the presence of scar tissue could be a hindrance to fertility. The hysteroscopy and laparoscopy procedures spotlight and treat anomalies like these.
TUBAL INFERTILITY
For women whose fallopian tubes are blocked at the uterine openings, natural conception may be hampered. By sliding fine tools through a hysteroscope, your fertility consultant may be able to open the fallopian tubes.
RECURRENT MISCARRIAGES
Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy procedures are also recommended if you have experienced recurrent miscarriages, or house small fibroids or polyps in your uterus. On Cloudnine, these twin techniques are useful tools in gauging the cause of infertility.
 Pap smear
Pap smear
Pap smear or Pap test is performed to check for cervical cancer in females. Pap smear involves the scraping of the cells from the cervix, which is a narrow, lower end of the uterus, present at the top of the vagina. This collection of cells sample is then sent to the lab to be reviewed under the microscope. The Pap smear test enables the physician to make an intervention and thereby helps in curing cervical cancer, if detected at an early stage. This test may also detect the risk of developing cervical cancer sometime in the future or detect any other relevant changes in the cells present in the cervix. The Pap test is an important step in the early diagnosis of developing cancer. Pap test is a quick, simple and painless screening test and is usually advised for every woman between the age range of 21 and 65 years.
Why it’s done?
A Pap test is usually performed with the pelvic examination. In the women above 30 years, Pap test is combined with a test for HPV i.e. human papillomavirus. This is a sexually transmitted disease-causing virus that can lead to cervical cancer in many women.
Usually, the doctor and the patient decide on when to undergo the Pap test and how frequently it should be done. The doctors generally advised going for Pap smear at the age of 21 years and then once every 2 to 3 years. In the women aged 30 years or above, the doctor advises the Pap test every 3 years or 5 years, in combination with the HPV test. In some cases, if the woman has certain risk factors for developing cervical cancer, the doctor can suggest a Pap test more frequently. Some of the factors, which can increase the risk of cervical cancer include:
- A diagnosis of cancer of the cervix or a previous Pap test that showed some precancerous cells.
- An HIV infection in a woman
- Exposure to DES i.e. diethylstilbestrol, before birth.
- Weak immune system due to the organ transplant, chronic use of corticosteroid or chemotherapy.
There are certain cases, wherein patients do not require pap test, as mentioned below.
- After the total hysterectomy procedure – After the removal of the uterus and the cervix of the woman, the patient should consult the doctor if the Pap test is to be continued. In case, the surgical procedure of hysterectomy was conducted to eliminate the non-cancerous lesions, then the routine Pap test can be discontinued. However, if the hysterectomy procedure was conducted for a cancerous or precancerous lesion, then the doctor advises to continue undergoing Pap test regularly.
Age factor – Older women can discontinue routine Pap testing. In the women aged 30 years or above, the doctor generally advises the Pap test every 3 years or 5 years, in combination with the HPV test. However, after the age of 65 years, and in case of normal screening results, the patient might be advised to stop the Pap test.
 Gynaecology
Gynaecology
Diagnosis and treatment of pre and post pregnancy concerns and female reproductive health,broad spectrum of women health care services involving unborn children and pregnant women along with efficient management of related diseases. Renders state-of-the-art technologies with superlative care providing a full range of healthcare services such as painless deliveries, minimally invasive surgeries, management of high-risk pregnancies/late pregnancies,
Women of different age groups have different health concerns, which are appropriately assessed and addressed with the utmost care. We provide comprehensive treatment for fibroids including open myomectomies unsuitable for endoscopic (keyhole) surgery. Ensures the total safety and comfort of women patient as well as their children. Procedures are completely safe and are well tested. The procedures performed include amniocentesis, Ultrasonography and chorionic villus sampling, which help in early detection of many problems. Focuses on expert counseling and quality care on matters related to infertility management, family welfare, menopause management, prenatal diagnosis, reconstructive surgery and pelvic floor medicine..
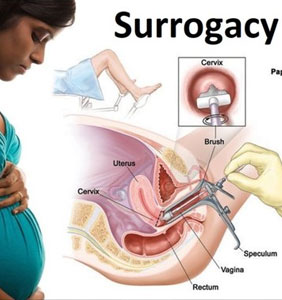 Surrogacy is a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to carry a full term pregnancy. There are two types of surrogacy, traditional and gestational surrogacy. Under traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is artificially inseminated with the father’s sperm whereas in gestational surrogacy the biological parents will remain the donors of the egg and the sperm.
Surrogacy is a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to carry a full term pregnancy. There are two types of surrogacy, traditional and gestational surrogacy. Under traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is artificially inseminated with the father’s sperm whereas in gestational surrogacy the biological parents will remain the donors of the egg and the sperm.
Why it’s Done
Surrogacy can be considered in cases where pregnancy is too risky to be carried by the biological mother, there are medical issues with the uterus or the mother has conditions that can make pregnancy life-threatening.
One can also opt for surrogacy if they are a single father or are not able to get pregnant with a variety of assisted-reproduction techniques, such as IVF.
What you can expect
Like any pregnancy, surrogacy has its own journey, hence the one thing to do is to be there emotionally and financially for the surrogate bearing the baby.
Soon after giving birth, the most optimum arrangement is to allow the baby unlimited access to the birth mother. Mother’s milk is of paramount importance to the growing baby. With the availability of breast pumps, it is possible to give mother’s milk to the baby even if the surrogate is not physically around.
Results
In case of a successful pregnancy, the biological parents will need to take care of the surrogate by taking her to an obstetrician for prenatal care.
After childbirth, the parents need to stay in touch with the surrogate to help her through postpartum issues.
What Are the Risks?
Surrogacy is a safe option to have a child and it has a high success rate. But with all its benefits, parents need to be aware of the risks that are associated with surrogacy. Here are the risks that involve surrogacy:
Infection
Chances are that the surrogate could experience cramping or bleeding after the procedure. The surrogate might also have to inject herself with hormone injections that can lead to allergies.
Transmission of Disease
Sometimes biological parents do not undergo screening processes for genetic diseases. Since the biological mother’s oocyte is in the uterus of the surrogate. Transmission of the infectious disease is possible and can be risky. If the surrogate is at risk, she might end the pregnancy.
Safety
A couple may ask their family members or close friends to act as surrogates. Although it might work for some, experts advise otherwise. There is no safety net if one of the parties backs out of the agreement.
The Uterine Scratch is a very minimal “procedure,” where the physician “scratches,” or takes an endometrial biopsy of the uterine cavity just prior to the menstrual cycle. Most commonly this is done before a cycle in which the patient will undergo IVF, but also with other fertility treatments like IUI or medicated intercourse.
The procedure is often done for those who have failed a or numerous cycles however some people do indeed choose to have it done in preparation for their first IVF treatment cycle.
The procedure requires no anesthesia and takes only 5 minutes. Due to the mild discomfort of the surgery, it may be suggested that you take Advil or Motrin approximately one hour before the procedure.
 Genetic evaluation
Genetic evaluation
Genetic evaluation is part of routine prenatal care and is ideally done before conception. The extent of genetic evaluation a woman chooses is related to how the woman weighs factors such as
- The probability of a fetal abnormality based on risk factors and the results of any previous testing
- The probability of a complication from invasive fetal testing
- The importance of knowing the results (eg, would the pregnancy be terminated if an abnormality was diagnosed, would not knowing the results cause anxiety)
 Male Infertility
Male Infertility
Infertility, the inability to get pregnant after 6-12 months of unprotected intercourse, is troubling, but not untreatable.
Male infertility is an issue for approximately one-half of couples seeking treatment, and most affected patients are asymptomatic.
Just as we do with our female patients, the first step in the male evaluation involves a thorough health history. This may reveal obvious barriers to getting pregnant: such as inherited conditions like cystic fibrosis, anatomic problems like a varicocoele, sexual function issues, obesity, or signs of hormonal deficiencies.
What to Expect During a Male Infertility Evaluation
A semen analysis involves collecting a semen sample, to assess sperm concentration, morphology (shape), and motility (ability to swim).
-
- Scrotal ultrasound.This test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images inside your body. A scrotal ultrasound can help your doctor see if there is a varicocele or other problems in the testicles and supporting structures.
- Transrectal ultrasound.A small, lubricated wand is inserted into your rectum. It allows your doctor to check your prostate and look for blockages of the tubes that carry semen.
- Hormone testing.Hormones produced by the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and testicles play a key role in sexual development and sperm production. Abnormalities in other hormonal or organ systems might also contribute to infertility. A blood test measures the level of testosterone and other hormones.
- Post-ejaculation urinalysis.Sperm in your urine can indicate your sperm are traveling backward into the bladder instead of out your penis during ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation).
- Genetic tests.When sperm concentration is extremely low, there could be a genetic cause. A blood test can reveal whether there are subtle changes in the Y chromosome — signs of a genetic abnormality. Genetic testing might be ordered to diagnose various congenital or inherited syndromes.
- Testicular biopsy.This test involves removing samples from the testicle with a needle. If the results of the testicular biopsy show that sperm production is normal your problem is likely caused by a blockage or another problem with sperm transport.
- Specialized sperm function tests.A number of tests can be used to check how well your sperm survive after ejaculation, how well they can penetrate an egg, and whether there’s any problem attaching to the egg. These tests aren’t often used and usually don’t significantly change recommendations for treatment.
 Recurrent pregnancy loss is classically defined as the occurrence of three or more consecutive pregnancy loss.A pregnancy loss is defined as a clinically-recognized pregnancy involuntarily ending before 20 weeks. A clinically-recognized pregnancy means that the pregnancy has been visualized on an ultrasound or that pregnancy tissue was identified after a pregnancy loss.
Recurrent pregnancy loss is classically defined as the occurrence of three or more consecutive pregnancy loss.A pregnancy loss is defined as a clinically-recognized pregnancy involuntarily ending before 20 weeks. A clinically-recognized pregnancy means that the pregnancy has been visualized on an ultrasound or that pregnancy tissue was identified after a pregnancy loss.
Most pregnancy losses result from chromosomal, or genetic, abnormalities, and are random events. The abnormality may come from the egg, the sperm, or the early embryo.
Treatment for recurrent miscarriage
Surgery can fix problems with a septate uterus and can eliminate some fibroids or scar tissue irregularities. Surgical correction is often the treatment of choice for anatomical issues since it improves live birth rates.
If the patient has an autoimmune problem, such as APS, a doctor may prescribe blood thinning medications such as a low-dose aspirin or heparin. Although a patient can take blood thinning medications during pregnancy to lower the risk of a miscarriage, she should talk with a doctor before using them, due to the increased chance of serious bleeding problems.
If a doctor finds a chromosomal problem such as translocation, he or she may recommend genetic counseling. While many couples with translocations conceive a healthy pregnancy naturally, a doctor might suggest fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), a process in which a reproductive specialist combines eggs and sperm in a lab. The embryos can then be genetically tested using a technique called preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), and only normal ones are transferred to the uterus. This improves pregnancy outcome.
 Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is a problem that can happen during any phase of the sexual response cycle. It prevents you from experiencing satisfaction from sexual activity
Sexual dysfunction generally is classified into four categories:
- Desire disorders: lack of sexual desire or interest in sex.
- Arousal disorders: inability to become physically aroused or excited during sexual activity.
- Orgasm disorders: delay or absence of orgasm (climax).
- Pain disorders: pain during intercourse.
Men and women with hormone deficiencies may benefit from hormone shots, pills.
Mechanical aids: Aids such as vacuum devices and penile implants may help men with erectile dysfunction (the inability to achieve or maintain an erection).
Sex therapists can people experiencing sexual problems that can’t be addressed by their primary clinician. Therapists are often good marital counselors, as well.
Psychotherapy: Therapy with a trained counselor can help you address sexual trauma from the past, feelings of anxiety, fear, guilt and poor body image.



